Blunt Force Trauma Care Pune
24×7 emergency trauma care in Pune for blunt force injuries. Expert team ensures accurate diagnosis and fast treatment.
Overview
Blunt force trauma occurs when the body experiences impact from a non-sharp object or surface, causing tissues to compress, stretch, or tear without creating an open wound. This type of injury is particularly deceptive because the external appearance may not reflect the severity of internal damage. The difference between blunt and sharp force trauma lies in the mechanism of injury: while sharp force trauma creates cuts or punctures that penetrate the skin, blunt force trauma damages underlying tissues through compression and deceleration forces.
These injuries are incredibly common, resulting from everyday accidents, sports activities, motor vehicle collisions, and workplace incidents. The challenge with blunt force trauma injuries is that they can affect multiple organ systems simultaneously, and the full extent of damage may not be immediately apparent, making early medical evaluation crucial.
Symptoms
The symptoms of blunt force trauma vary significantly depending on the location, force of impact, and affected organs. Recognizing these signs early is vital for proper treatment:
- Immediate symptoms include pain, swelling, and visible bruising at the impact site
- Difficulty breathing or chest pain, which may indicate lung or rib injuries
- Abdominal pain or rigidity, potentially signaling internal organ damage
- Confusion, dizziness, or loss of consciousness following head impact
- Nausea and vomiting, particularly after head or abdominal trauma
- Rapid heart rate and low blood pressure, suggesting internal bleeding
- Pale, clammy skin indicating possible shock
- Limited range of motion or visible deformity in affected limbs
It’s important to note that some symptoms may appear hours or even days after the initial injury. Any persistent or worsening symptoms require immediate medical attention, as delayed presentation can indicate serious complications.
Causes
Blunt force trauma can result from numerous scenarios in daily life:
- Motor vehicle accidents remain the leading cause, involving cars, motorcycles, bicycles, and pedestrian incidents. The rapid deceleration and impact forces in these accidents often cause multiple blunt force trauma injuries simultaneously.
- Falls from heights or onto hard surfaces are particularly common among children and elderly individuals.
- Sports-related injuries, especially in contact sports like football, hockey, and martial arts, frequently result in blunt force trauma.
- Physical altercations involving punches, kicks, or impacts with blunt objects also contribute significantly to these injuries.
- Workplace accidents in construction, manufacturing, and industrial settings pose ongoing risks, while recreational activities and home accidents round out the common causes of blunt force trauma.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of experiencing blunt force trauma or suffering more severe consequences:
- Age plays a significant role, with children having more flexible but vulnerable bones and tissues, while older adults face increased risk due to brittle bones, slower reflexes, and pre-existing health conditions.
- Participation in high-risk activities, contact sports, or occupations involving heavy machinery elevates exposure risk.
- Medical conditions such as osteoporosis, bleeding disorders, or the use of blood-thinning medications can worsen outcomes.
- Substance use, including alcohol and drugs, impairs judgment and reaction time, increasing both the likelihood of accidents and the severity of resulting injuries.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing blunt force trauma requires a comprehensive approach combining clinical assessment with advanced imaging:
Healthcare providers begin with a detailed history of the incident, including the mechanism of injury, force involved, and time elapsed since the trauma.
Physical examination focuses on identifying external signs of injury while assessing for internal damage through palpation, listening to heart and lung sounds, and neurological evaluation.
Imaging studies form the backbone of diagnosis:
- X-rays detect bone fractures and some internal injuries
- Ultrasound quickly identifies internal bleeding, particularly in abdominal trauma
- CT scans provide detailed images of internal organs, brain, chest, and abdomen
- MRI offers superior soft tissue visualization for complex injuries
Laboratory tests, including blood counts and chemistry panels, help assess for internal bleeding, organ function, and overall physiological status.
In emergency situations, rapid assessment protocols prioritize life-threatening conditions before comprehensive diagnostic workup.
Types
Blunt force trauma injuries encompass various patterns of tissue damage:
| Type | Description | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Contusion | Bruising from blood vessel damage beneath intact skin | Black-and-blue marks after a fall |
| Abrasion | Scraping of the skin due to friction | Road rash from a bike accident |
| Laceration | Tearing of skin/tissue from blunt impact | Split skin from hitting a hard object |
| Hematoma | Localized blood collection outside blood vessels | Bump on the head after impact |
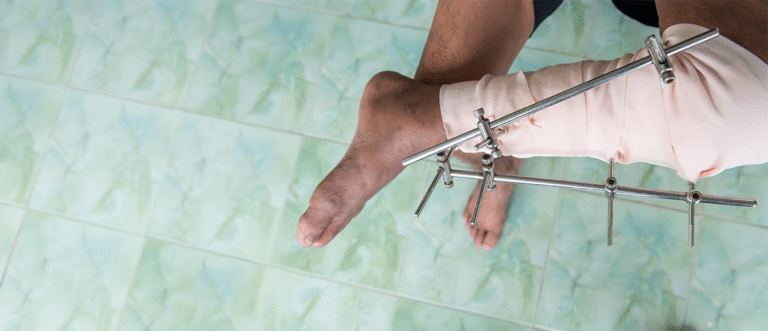
| Fracture | Broken bone due to force | Broken arm in a car crash |
| Organ injury | Damage to internal organs (liver, spleen, brain, lungs, etc.) | Spleen rupture from a fall |
| Crush injury | Compression of body part causing tissue and muscle damage | Limb trapped under heavy object |
- Stab wounds typically create a narrow wound channel with damage primarily along the path of penetration. The injury pattern is usually predictable based on the weapon’s size and the angle of attack.
- Projectile injuries from bullets or shrapnel create more complex damage patterns due to high velocity and energy transfer. These injuries often cause damage beyond the direct path of the projectile through shock waves and tissue cavitation.
- Impalement injuries present unique challenges because the embedded object may be providing pressure to control bleeding from damaged blood vessels. Removal requires careful surgical planning to prevent massive hemorrhage.
- Bite wounds carry high infection risk due to bacteria in the animal’s mouth and often create irregular, torn wound patterns that are difficult to clean thoroughly.
Treatment
Blunt force trauma treatment depends heavily on the severity, location, and type of injury sustained. Treatment approaches range from simple first aid to complex surgical interventions:
Emergency Care: Initial management focuses on stabilizing life-threatening conditions. Emergency responders assess airway, breathing, and circulation while controlling external bleeding and immobilizing suspected fractures. Rapid transport to appropriate medical facilities is crucial for severe cases.
Medical Management:
- Pain control using appropriate analgesics
- Wound care for external injuries, including cleaning and dressing
- Immobilization of fractures using casts, splints, or surgical fixation
- Monitoring for developing complications or delayed presentations
Surgical Intervention: Severe blunt force trauma injuries may require immediate surgery:
- Abdominal surgery for organ repair or removal
- Neurosurgery for traumatic brain injuries with increased intracranial pressure
- Orthopedic surgery for complex fractures
- Thoracic surgery for chest injuries affecting lungs or heart
Supportive Care:
- Blood transfusions for significant blood loss
- Mechanical ventilation for respiratory compromise
- Intensive care monitoring for unstable patients
Rehabilitation
Recovery from significant blunt force trauma often requires comprehensive rehabilitation programs tailored to individual needs:
- Physical Therapy focuses on restoring strength, flexibility, and coordination through targeted exercises and movement therapy.
- Occupational therapy helps patients regain skills for daily living activities and adapt to any lasting disabilities.
Complications
Blunt force trauma can lead to various short-term and long-term complications:
- Immediate complications include internal bleeding leading to shock, organ failure, and death if not promptly treated. Compartment syndrome occurs when pressure builds within muscle compartments, potentially causing tissue death.
- Long-term complications may include chronic pain, permanent disability, organ dysfunction, and psychological trauma. Infections can develop, particularly if surgery is required or if skin integrity is compromised.
Prevention
While not all blunt force trauma is preventable, many injuries can be avoided through safety measures:
- Vehicle Safety: Always use seat belts, ensure proper child safety seat installation, and avoid distracted or impaired driving. Regular vehicle maintenance and adherence to traffic laws significantly reduce accident risk.
- Sports and Recreation: Wear appropriate protective equipment, follow safety rules, and ensure proper training and supervision. Choose activities appropriate for your skill level and physical condition.
- Home Safety: Install safety features like handrails, non-slip surfaces, and adequate lighting. Keep walkways clear and maintain equipment properly.
- Workplace Safety: Follow all safety protocols, use required protective equipment, and participate in safety training programs.
Living With Blunt Force Trauma
Recovery from blunt force trauma varies dramatically among individuals. Some people heal quickly with minimal intervention, while others face lengthy recovery periods with ongoing challenges.
- Successful recovery requires active participation in medical care, including attending all follow-up appointments and adhering to treatment recommendations.
- Engaging fully in rehabilitation programs maximizes functional recovery and helps prevent secondary complications.
- Monitoring for delayed symptoms is crucial, as some complications may not appear immediately.
- Maintaining open communication with healthcare providers ensures any new problems are addressed promptly.
- Emotional support from family, friends, and mental health professionals plays a vital role in recovery.
Key Takeaways
- Blunt force trauma results from non-penetrating impacts that can cause serious internal injuries even when external wounds appear minor
- The difference between blunt and sharp force trauma lies in the mechanism of injury, with blunt trauma causing damage through compression and deceleration forces rather than penetration
- Blunt force trauma injuries can affect multiple organ systems and may have delayed presentations, making prompt medical evaluation essential
- Blunt force trauma treatment ranges from supportive care to complex surgical interventions, depending on injury severity and location
- Prevention through safety measures significantly reduces the risk of these potentially life-threatening injuries
- At Sancheti Hospital, our experienced trauma team provides comprehensive care for blunt force trauma patients, utilizing advanced diagnostic tools and treatment protocols to ensure optimal outcomes and support patients through every stage of recovery
Patient Stories & Experiences


The pain in my left knee left me feeling helpless for years. After my treatment here, I can finally say I'm pain-free.
Vinita Singh


The nerves were swollen, and the body went numb. But thanks to Sancheti Hospital, I got a second life!
Parvati


I finally could walk again, a relief I've only felt after the hip pain surgery. I thank the doctors at Sancheti Hospital for their help.
Balaji Kharat


I'm a police officer, and I'm extremely thankful to Sancheti Hospital for treating my fracture without surgery.
Shantilal


My life has completely changed after the knee replacement surgery at Sancheti Hospital. It's like I can finally live again!
Kalpana Lepcha


The knee pain I've carried for years finally went away with the help of Sancheti Hospital.
Karuna


I can't believe that I get to finally live a normal and happy life, all thanks to the knee surgery I had at Sancheti Hospital.
Kishore Bhosle
Other Conditions
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I tell if blunt force trauma has caused internal injuries?
Internal injuries may not be immediately obvious. Watch for symptoms like persistent pain, swelling, difficulty breathing, abdominal tenderness, dizziness, or changes in mental status. When in doubt, seek medical evaluation immediately.
What is the most dangerous type of blunt force trauma?
Head and abdominal injuries are particularly concerning due to their potential for life-threatening complications. Brain injuries can cause swelling and increased pressure, while abdominal trauma can lead to internal bleeding from organ damage.
How long does recovery from blunt force trauma typically take?
Recovery time varies greatly depending on injury severity and location. Minor bruises may heal within days, while severe injuries requiring surgery can take months of treatment and rehabilitation.
Can blunt force trauma cause delayed symptoms?
Yes, some symptoms may not appear for hours or days after the initial injury. This is particularly common with head injuries and internal bleeding, which is why medical monitoring is often necessary even for seemingly minor trauma.
When should I seek emergency care for blunt force trauma?
Seek immediate emergency care for any significant impact to the head, chest, or abdomen, loss of consciousness, difficulty breathing, severe pain, visible deformity, or signs of shock such as rapid pulse, dizziness, or pale skin.

 Home
Home Patient Login
Patient Login International patients
International patients Contact Us
Contact Us Emergency
Emergency Download Reports
Download Reports